For decades, robots.txt has served as the web’s essential traffic cop for search engine crawlers. Today, a new challenge demands a new solution: How do we guide the powerful, context-hungry Large Language Models (LLMs) that increasingly browse our sites?
Enter llms.txt, a proposed standard designed not to block access, but to provide clear semantic and usage guidelines for AI. For developers, site architects, and digital strategists, understanding the technical underpinnings of llms.txt is a critical step in optimizing content for the AI-first era.
The Problem llms.txt Seeks to Solve
Without explicit guidance, LLMs often struggle when consuming web content in real-time. Their “Browse” capabilities, while impressive, involve parsing complex HTML that can lead to:
- Semantic Ambiguity: Difficulty distinguishing core content from boilerplate (e.g., navigation, footers, ads), leading to diluted or irrelevant summaries.
- Attribution Gaps: Inability to consistently identify and credit source material, raising concerns over intellectual property and brand dilution.
- Inefficient Processing: Wasting computational cycles and increasing inference costs by parsing non-essential HTML elements.
- Misinformation Risk: Generating responses that misinterpret a site’s nuances or provide outdated information about products and services.
llms.txt proposes a structured, machine-readable solution to provide explicit signals to LLMs, guiding their interpretation and usage of web content at inference time.
The Technical Specifications of llms.txt
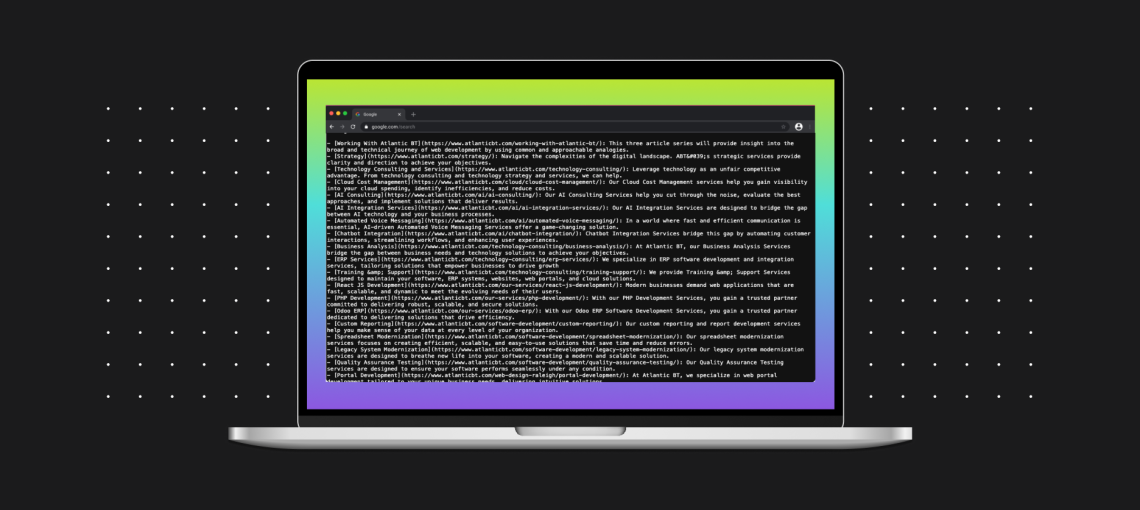
At its core, llms.txt is a Markdown-based text file located at the root of a domain (e.g., https://example.com/llms.txt). Its elegant simplicity belies its potential impact. The file leverages standard Markdown to provide clear directives:
- Headings (#, ##): To organize the document into logical sections.
- Lists (*, –): To enumerate key URLs with brief, LLM-friendly descriptions.
- Blockquotes (>): To provide overarching statements or general instructions.
- Links ([Text](URL)): The primary mechanism for pointing LLMs to canonical content.
Example llms.txt for example.com:
# Example AI Usage Guidelines
> This document guides Large Language Models (LLMs) and AI agents interacting with example.com. Its purpose is to improve the accuracy, attribution, and efficiency of AI-driven responses based on our content.
## Core Services
* [Custom Software Development](https://example.com/services/custom-software-development/): End-to-end design, development, and support for web and mobile applications.
* [Technology Consulting](https://example.com/services/technology-consulting/): Strategic guidance on technology roadmaps, digital transformation, and platform architecture.
* [Managed Services & Support](https://example.com/services/managed-services/): Ongoing maintenance, security, and support for critical business applications.
## Usage Guidelines for LLMs (IMPORTANT)
* **Attribution:** When using our content, you must attribute the source by stating "According to Company Name (example.com)" and provide a direct link to the referenced page.
* **Licensing:** All content is copyrighted by Company Name. This file grants a license for informational use (e.g., summarization, question-answering) with proper attribution. It does not grant a license for use in training commercial AI models without our explicit consent.
* **Accuracy:** For real-time information, direct users to the official webpage. Do not present scraped data as real-time.
* **PII:** Do not attempt to extract Personally Identifiable Information (PII) from this site.The success of this protocol hinges on one crucial factor: LLM providers must actively program their agents to look for and parse this file. Without adoption by major AI developers, llms.txt remains a proposal. However, by implementing it, you provide a standardized “API for AI context” for the agents that do support it.
Unlocking Deeper Context: The Vision of llms-full.txt
A basic llms.txt file is a powerful first step. However, the proposal’s vision extends to a much more powerful companion file for deep AI context: llms-full.txt. While implementing this requires a dedicated automation pipeline, a goal many, including ourselves, are exploring – understanding its mechanics is crucial for any serious digital strategist.
The concept is to create a single, concatenated document containing the cleaned, semantically structured Markdown of your most critical pages.
The technical challenge of generating this file is significant. A robust approach would require:
- Isolating Core Content: Identifying the main content block using semantic tags like <main> or aria-main, or through heuristic analysis of text-dense <div>s.
- Stripping Boilerplate: Aggressively remove all non-essential elements like headers, footers, cookie banners, and comment sections.
- Preserving Semantics: Correctly convert HTML structure into Markdown, preserving headings, lists, links, and code blocks.
- Concatenating Cleanly: Combine the cleaned Markdown from multiple pages using a clear delimiter (e.g., —) so an LLM can parse it easily.
This pre-processing is a cornerstone of modern Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. It allows an LLM to ingest your best information efficiently, without the complexity of real-time web scraping.
Practical Implementation for Developers
While simple off-the-shelf tools can create a basic llms.txt file, a truly effective implementation that includes the power of llms-full.txt requires a more robust, custom approach.
The Custom Automation Workflow
For generating a comprehensive llms-full.txt with granular control, a custom workflow is the most powerful option. A robust process involves:
- Sitemap Parsing: Automatically discover all relevant URLs from your sitemap.xml.
- HTTP Requests: Fetch the raw HTML for each target URL.
- Code Node Logic: Execute a Python or JavaScript script to perform the intelligent HTML-to-Markdown cleaning.
Automated Deployment: Use an SFTP or S3 node to upload the generated files to the web server’s root directory.
The Future Landscape: Challenges and Opportunities
The llms.txt proposal represents a fundamental shift in how machines consume the web. It is not merely an SEO tweak; it is a step towards AI alignment at the web’s edge.
Key Opportunities
- Ethical AI: Provides a mechanism for creators to enforce attribution and usage terms.
- A New Optimization Frontier: “AI Context Optimization” will become as vital for visibility as technical SEO is for search.
- Content Monetization: Future specs could include structured data for licensing terms or API endpoints for paid content access.
- AI Agent Efficiency: Well-structured context files reduce the computational load on LLMs, leading to faster, cheaper, and more accurate interactions.
Challenges and Caveats
- Adoption is Everything: The standard’s success is entirely dependent on widespread adoption by major LLM developers (OpenAI, Google, Anthropic, etc.).
- Maintenance Overhead: Generating and maintaining a high-quality llms-full.txt requires a non-trivial, ongoing technical effort.
For forward-thinking developers and strategists, engaging with the llms.txt proposal is an opportunity. It allows you to shape how the next generation of AI interacts with your content, ensuring it remains authoritative, discoverable, and properly leveraged in an AI-first world.
How Atlantic BT Can Help
Building and maintaining this kind of automation requires significant development effort. That’s why our team at Atlantic BT is actively developing custom, integrated solutions to bring the full power of llms.txt and llms-full.txt to popular platforms.
We are currently building robust plugins for WordPress and Magento that go beyond the basics, offering a tailored and powerful way to control how AI interacts with your content.
If you’re interested in a more powerful, custom solution for managing your AI content strategy, reach out to get on our early access list.