What are Third-Party Cookies?
Third-party cookies are small text files created by domains other than the one you are directly visiting. There are various reasons they are used:
- Tracking and Analytics: Third-party cookies can track a user’s browsing activities across multiple websites. This data is valuable for analytics, helping website owners understand user behavior and improve their site’s performance and content.
- Advertising: Perhaps the most well-known use of these cookies is in targeted advertising. Advertisers use these cookies to gather information about your interests based on the sites you visit and the actions you take. This allows them to show you more relevant ads across different websites, attempting to increase engagement and conversion rates.
- Social Media Features: Websites might use them to enable social media functionalities, such as “Like” buttons, sharing capabilities, and other interactive elements that link back to social media platforms.
- Content Personalization: Similar to advertising, third-party cookies can be used to personalize content across websites. For example, a news site might modify what you see based on the articles you’ve read on other sites.
- Cross-Site Login: Some services use them to allow users to log in to various websites with the same credentials without having to authenticate separately on each site.
Why are Third-Party Cookies Being Phased Out?
Privacy.
Digital privacy has reached a tipping point and become a culturally visible concern. Companies compiling detailed personal profiles with cookies has raised alarms about individual privacy rights. Third-party cookies, which track users’ across different sites, often without explicit consent or clear understanding from users, is an example of the lack of digital privacy that affects anyone using a browser.
This has led to laws and regulations like GDPR in the EU and CCPA in California that put strict requirements on how personal data can be collected, processed, and stored; consent must be clear before data can be used, and users have more control of their personal data.
Effects of Removing
Removing third-party cookies will significantly affect how websites track user behavior across the internet. Currently, many businesses rely on these cookies for targeted advertising and analytics. Without these cookies:
- Advertisers will find it harder to track user behavior across multiple sites.
- Publishers may see a decrease in advertising revenue, since personalized ads tend to generate higher revenue.
- Users will likely notice a difference in how personalized their web experiences are, with potentially fewer targeted ads.
The Current State of Third-Party Cookies
Some browsers have already cut out third-party cookies by default. The notable ones are Firefox and Safari.
Some browsers are slowly moving towards removing them. They are Chrome and Edge.
Let’s look at browsers North American market share for the last year ending April 2024. Data from Statcounter Global Stats.
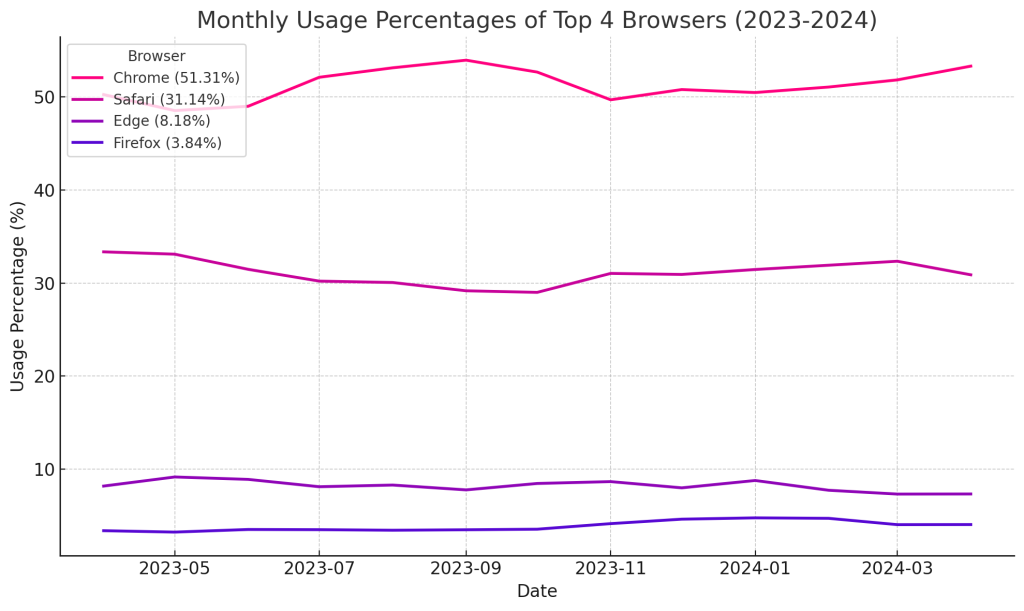
- The gorilla in the room is Chrome, with a 51% average market share over the year. They have a detailed and current plan (it has been delayed multiple times) to phase out third-party cookies by early 2025. No matter your site, if you use them you need to look into this as you most likely have a large chunk of Chrome users.
- The browser with the largest share of use and has blocked third-party cookies is Safari, with a 31% average market share over the year.
- Microsoft’s Edge browser has about an 8% average market share, but by default they currently don’t block these cookies. Users can manually set cookies to be blocked, and they have started the process of warning users and developers that third-party cookies will be phased out.
- Firefox has about a 4% average market share and also blocks these cookies by default.
Your specific site browser percentages may differ, but you may already have some motivation to start implementing alternatives to third-party cookies.
Do you need help? We can do a technical audit and start the conversation.